The orbital diagram for a ground state nitrogen atom is a fundamental concept in chemistry that unveils the intricate arrangement of electrons within the atom. This diagram serves as a roadmap to understanding the chemical properties and reactivity of nitrogen, an element that plays a vital role in various biological processes and industrial applications.
Through the exploration of the nitrogen atom’s orbital diagram, we embark on a journey into the quantum realm, where the fundamental principles governing the behavior of electrons dictate the atom’s electronic structure and its interactions with the surrounding environment.
1. Introduction

An orbital diagram is a graphical representation of the wave functions of electrons in an atom or molecule. It provides valuable insights into the electronic structure and properties of chemical species.
The purpose of analyzing the orbital diagram for a ground state nitrogen atom is to understand the distribution of electrons among its atomic orbitals and how this arrangement influences its chemical behavior.
2. Electron Configuration and Orbital Arrangement
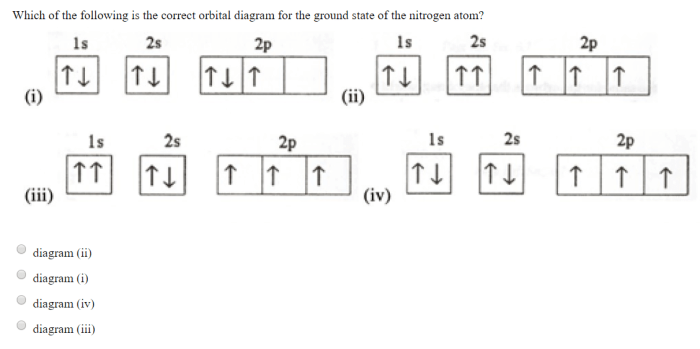
The electron configuration of a ground state nitrogen atom is 1s 22s 22p 3.
The electrons are distributed as follows:
- Two electrons in the 1s orbital
- Two electrons in the 2s orbital
- Three electrons in the 2p orbitals (one in each of the three p orbitals, px, py, and pz)
The orbital diagram for the ground state nitrogen atom is shown below:
3. Quantum Numbers and Orbital Properties
The quantum numbers are a set of four numbers (n, l, ml, and ms) that describe the properties of an electron in an atom.
- n (principal quantum number): Describes the energy level of the orbital.
- l (azimuthal quantum number): Describes the shape of the orbital.
- ml (magnetic quantum number): Describes the orientation of the orbital in space.
- ms (spin quantum number): Describes the spin of the electron.
The following table summarizes the quantum numbers and orbital properties for the nitrogen atom’s ground state:
| Orbital | n | l | ml | ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1s | 1 | 0 | 0 | +1/2,
|
| 2s | 2 | 0 | 0 | +1/2,
|
| 2px | 2 | 1 | -1 | +1/2,
|
| 2py | 2 | 1 | 0 | +1/2,
|
| 2pz | 2 | 1 | +1 | +1/2,
|
4. Molecular Orbital Theory and Bonding
Molecular orbital theory is a method used to describe the electronic structure of molecules. It explains how atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals, which are the orbitals that hold the electrons in a molecule.
In the case of the nitrogen molecule, the 2p orbitals of the two nitrogen atoms overlap to form two molecular orbitals: a bonding orbital (σ 2p) and an antibonding orbital (σ* 2p).
The bonding orbital is lower in energy than the atomic orbitals, while the antibonding orbital is higher in energy. The two electrons from the nitrogen atoms occupy the bonding orbital, resulting in a strong bond between the atoms.
The molecular orbital diagram for the nitrogen molecule is shown below:
5. Applications and Implications: The Orbital Diagram For A Ground State Nitrogen Atom Is
Understanding the orbital diagram of a nitrogen atom has numerous practical applications:
- Predicting chemical reactivity: The orbital diagram can be used to predict the reactivity of a nitrogen atom by examining the number and arrangement of its electrons.
- Molecular properties: The orbital diagram can be used to explain various molecular properties, such as bond length, bond strength, and molecular shape.
- Applications in fields such as chemistry, materials science, and nanotechnology: The knowledge of orbital diagrams is essential for understanding and developing new materials, designing catalysts, and studying chemical reactions.
Essential FAQs
What is the electron configuration of a ground state nitrogen atom?
1s2 2s2 2p3
How many valence electrons does a nitrogen atom have?
5
What is the significance of the orbital diagram in chemistry?
It provides a visual representation of the electronic structure of an atom or molecule, which helps predict chemical properties and reactivity.