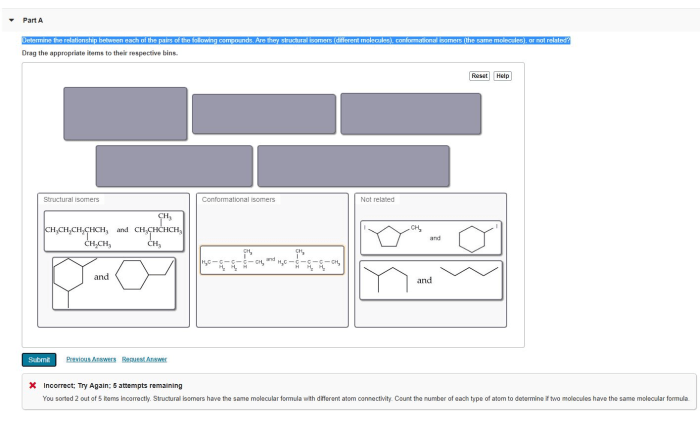
In chemistry, structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of their atoms. This fascinating topic, which of the following pairs of compounds are structural isomers, delves into the significance and identification of structural isomers, exploring their impact on various fields.
Structural isomers arise due to the distinct ways in which atoms can be connected within a molecule. Understanding these isomers is crucial for comprehending chemical reactions, predicting product outcomes, and unlocking the potential of isomerism in diverse applications.
Structural Isomers
Structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of their atoms. This difference in arrangement can lead to significant differences in their physical and chemical properties.Structural isomers are important because they can have different biological activities and different chemical reactivity.
For example, the isomers of glucose have different sweetness and different rates of metabolism. The isomers of butane have different boiling points and different octane ratings.
Identifying Structural Isomers
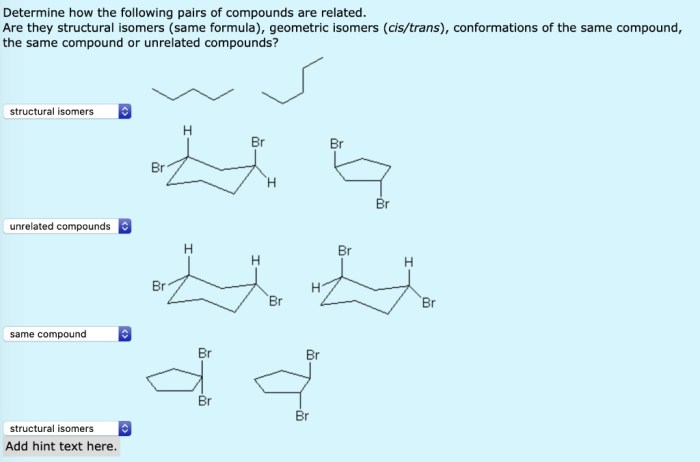
There are a number of ways to identify structural isomers. One way is to use the molecular formula of the compounds. If two compounds have the same molecular formula, then they are isomers. Another way to identify structural isomers is to use their connectivity.
Connectivity refers to the way that the atoms in a molecule are connected to each other. If two compounds have the same molecular formula but different connectivity, then they are isomers.The following is a step-by-step procedure for determining if two compounds are structural isomers:
- Determine the molecular formula of each compound.
- If the molecular formulas are the same, then the compounds are isomers.
- If the molecular formulas are different, then the compounds are not isomers.
- If the molecular formulas are the same, then compare the connectivity of the atoms in each compound.
- If the connectivity is the same, then the compounds are isomers.
- If the connectivity is different, then the compounds are not isomers.
Types of Structural Isomers
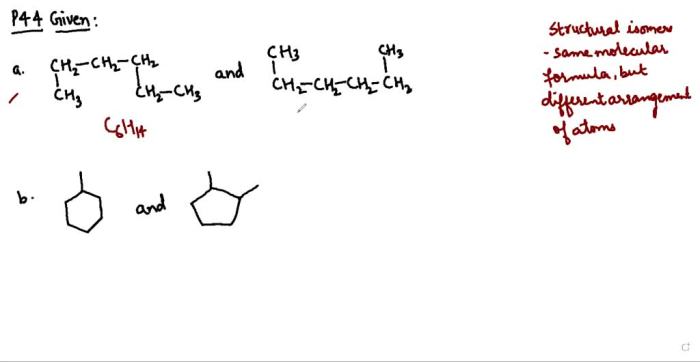
There are three main types of structural isomers:
1. Chain isomers
Chain isomers have the same molecular formula and the same functional groups, but the atoms are arranged in different chains. For example, butane and isobutane are chain isomers.
2. Position isomers
Position isomers have the same molecular formula and the same functional groups, but the functional groups are attached to different atoms in the chain. For example, 1-butanol and 2-butanol are position isomers.
3. Functional group isomers
Functional group isomers have the same molecular formula, but they have different functional groups. For example, butanol and diethyl ether are functional group isomers.
Applications of Structural Isomerism
Structural isomerism has a number of applications in chemistry, biology, and medicine. In chemistry, structural isomerism is used to design new materials with specific properties. In biology, structural isomerism is used to understand the structure and function of biomolecules. In medicine, structural isomerism is used to design new drugs with specific activities.
FAQs: Which Of The Following Pairs Of Compounds Are Structural Isomers
What are structural isomers?
Structural isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different atomic arrangements.
How do you identify structural isomers?
Structural isomers can be identified by comparing their molecular formulas and connectivity.
What is the significance of structural isomerism?
Structural isomerism has implications for physical and chemical properties, drug development, material science, and industrial processes.