Art-labeling activity: development and nutritive functions of the placenta – The art-labeling activity on the development and nutritive functions of the placenta invites you on an intriguing journey into the depths of human reproduction. This activity aims to illuminate the crucial role of the placenta, a remarkable organ that fosters the growth and nourishment of a developing fetus.
Join us as we delve into the intricacies of placental structure, its pivotal role in nutrient exchange, and its hormonal contributions to a healthy pregnancy.
Introduction
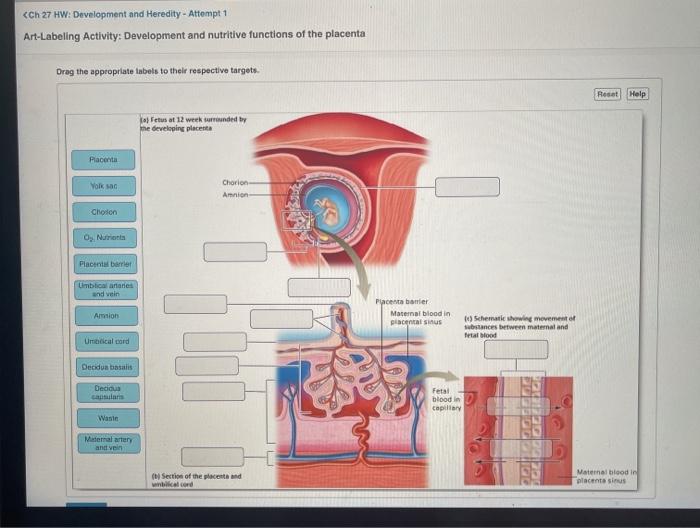
The placenta, a crucial organ that forms during pregnancy, plays a vital role in the development and nourishment of the fetus. It serves as a bridge between the mother and the developing baby, facilitating the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products.
Placental Structure and Development
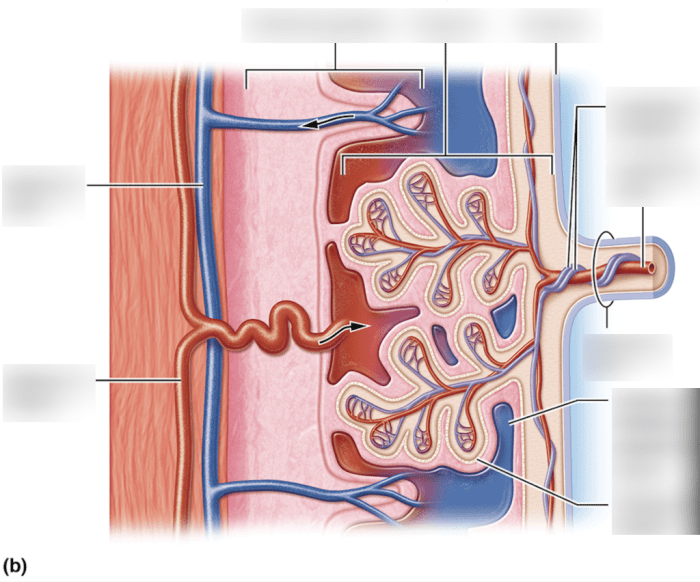
The placenta is composed of two main components: the maternal decidua and the fetal chorion. The maternal decidua is the modified uterine lining, while the fetal chorion is derived from the embryonic membranes. These two layers are separated by the intervillous space, which contains maternal blood sinuses.
As the pregnancy progresses, the placenta undergoes significant structural changes to accommodate the growing needs of the fetus.
Nutrient Exchange across the Placenta
The placenta plays a critical role in the exchange of nutrients between the mother and the fetus. Oxygen and nutrients from the maternal blood diffuse across the placental membrane into the fetal circulation, while fetal waste products diffuse in the opposite direction.
This exchange is facilitated by a number of mechanisms, including simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport.
Hormonal Functions of the Placenta
In addition to its role in nutrient exchange, the placenta also produces a variety of hormones that are essential for maintaining pregnancy and fetal development. These hormones include human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which maintains the corpus luteum and supports progesterone production, and human placental lactogen (hPL), which promotes fetal growth and development.
Placental Adaptations to Support Fetal Growth
As the fetus grows, the placenta undergoes a series of adaptations to meet the changing needs of the developing baby. These adaptations include an increase in the surface area for nutrient exchange, an increase in the number of blood vessels, and an increase in the production of hormones.
Clinical Significance of Placental Function, Art-labeling activity: development and nutritive functions of the placenta
Placental dysfunction can have serious implications for fetal development and pregnancy outcomes. Placental abnormalities can lead to a variety of complications, including fetal growth restriction, premature birth, and stillbirth. Therefore, monitoring placental function is an important part of prenatal care.
Q&A: Art-labeling Activity: Development And Nutritive Functions Of The Placenta
What is the significance of the placenta in pregnancy?
The placenta serves as a lifeline between the mother and the developing fetus, facilitating the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste products.
How does the placenta contribute to fetal development?
The placenta provides essential nutrients and oxygen to the fetus, while removing waste products. It also produces hormones that support pregnancy and fetal growth.
What are the different layers of the placenta?
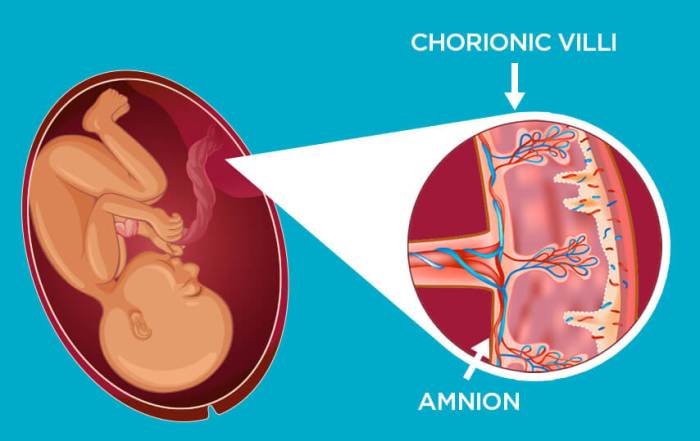
The placenta consists of three main layers: the maternal decidua, the chorion, and the amnion. Each layer plays a specific role in nutrient exchange and fetal protection.