The customers’ customer is upstream in the supply chain – In today’s interconnected business landscape, understanding the customer’s customer is paramount for supply chain success. The customer’s customer, located upstream in the supply chain, exerts a profound influence on customer satisfaction and overall business outcomes.
This comprehensive analysis explores the concept of the customer’s customer, its significance in supply chain analysis, and the strategies for managing upstream relationships to enhance customer satisfaction.
Customer-centricity in Supply Chain Management

Customer-centricity is a strategic approach that places the customer at the heart of every decision and action within the supply chain. It involves understanding customer needs, wants, and expectations and aligning supply chain operations to meet those requirements effectively and efficiently.
Customer-centric practices in supply chains include:
- Collecting and analyzing customer data to gain insights into their preferences and behaviors
- Designing products and services that meet specific customer needs
- Providing excellent customer service and support throughout the customer journey
- Empowering employees to make decisions that enhance customer satisfaction
Benefits of implementing customer-centric approaches include:
- Increased customer satisfaction and loyalty
- Improved profitability and revenue growth
- Enhanced brand reputation and customer trust
- Reduced operational costs and improved efficiency
Challenges of implementing customer-centric approaches include:
- The need for a comprehensive understanding of customer needs
- The cost and complexity of collecting and analyzing customer data
- The potential for conflict between customer-centric and other business objectives
- The need for organizational change and employee buy-in
Identifying the Customer’s Customer
The customer’s customer is the end-user or recipient of the products or services provided by the customer. Identifying the customer’s customer is crucial in supply chain analysis as it helps organizations understand the ultimate purpose of their products or services and the value they provide to the end consumer.
Methods for identifying the customer’s customer include:
- Conducting market research to gather insights into the end-user’s demographics, needs, and behaviors
- Analyzing customer feedback and complaints to identify areas of dissatisfaction or unmet needs
- Observing the customer’s interactions with the product or service to understand how it is being used and what value it provides
Implications of considering the customer’s customer in supply chain decision-making include:
- Improved product and service design and development
- Enhanced marketing and communication strategies
- Optimized supply chain operations to meet the specific needs of the end consumer
- Increased customer satisfaction and loyalty
Upstream Influence on Customer Satisfaction
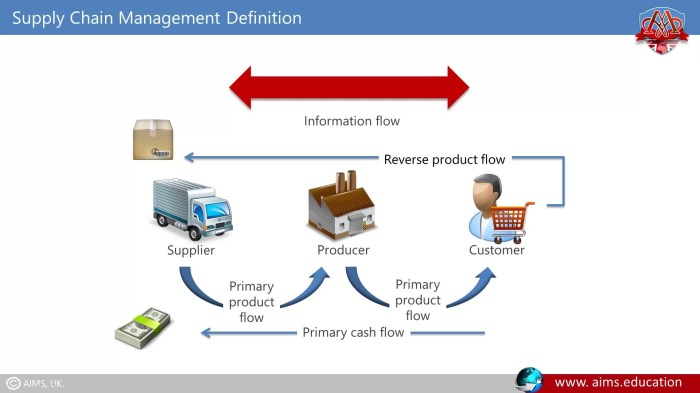
The actions and decisions of upstream suppliers can significantly impact customer satisfaction. Factors such as product quality, delivery timeliness, and cost can directly affect the customer’s experience with the final product or service.
Examples of upstream factors that can influence customer experiences include:
- Defective or substandard materials or components
- Delayed or unreliable deliveries
- Unexpected price increases
- Poor supplier communication or customer service
Strategies for managing upstream relationships to enhance customer satisfaction include:
- Establishing clear expectations and communication channels with suppliers
- Conducting regular supplier performance evaluations
- Providing training and support to suppliers to improve their quality and efficiency
- Developing contingency plans to mitigate the impact of potential supplier disruptions
Collaboration and Information Sharing: The Customers’ Customer Is Upstream In The Supply Chain
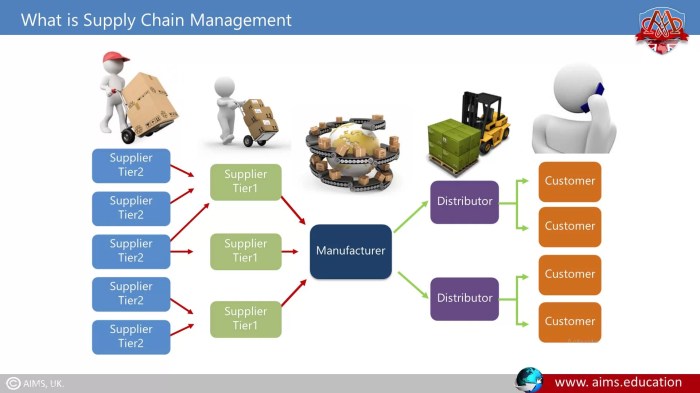
Collaboration and information sharing between upstream suppliers and downstream customers are crucial for enhancing customer satisfaction and achieving supply chain success.
Benefits of implementing collaborative supply chain models include:
- Improved product and service quality
- Reduced costs and increased efficiency
- Enhanced innovation and value creation
- Improved supply chain visibility and transparency
Challenges of implementing collaborative supply chain models include:
- The need for trust and commitment between partners
- The cost and complexity of implementing information sharing systems
- The potential for conflict between partners’ objectives
- The need for organizational change and employee buy-in
Examples of successful collaboration initiatives in different industries include:
- The automotive industry, where suppliers and manufacturers collaborate on product design and development
- The retail industry, where retailers and suppliers share data to improve inventory management and customer service
- The healthcare industry, where hospitals and medical device manufacturers collaborate on improving patient outcomes
Innovation and Value Creation
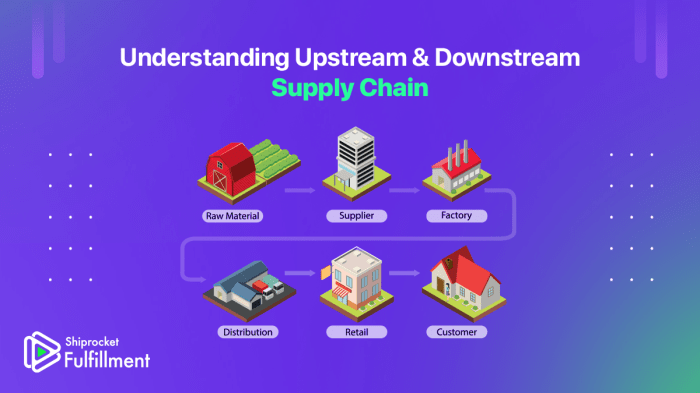
Innovation plays a critical role in creating value for both customers and their customers. Upstream suppliers can contribute to innovation and value creation by:
- Developing new products and technologies that meet evolving customer needs
- Improving the quality and efficiency of their products and services
- Collaborating with customers to develop innovative solutions
Examples of innovative solutions that have improved customer outcomes include:
- Self-driving cars that enhance safety and convenience
- Personalized medicine that improves patient outcomes and reduces costs
- Sustainable packaging solutions that reduce environmental impact
Risk Management and Supply Chain Resilience
Considering the customer’s customer in supply chain management introduces additional risks that need to be managed. These risks include:
- The potential for disruptions in the supply chain that can impact the customer’s customer
- The risk of reputational damage if the customer’s customer experiences dissatisfaction
- The risk of financial losses if the customer’s customer cancels orders or demands compensation
Strategies for managing these risks and enhancing supply chain resilience include:
- Conducting risk assessments to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities
- Developing contingency plans to mitigate the impact of potential disruptions
- Diversifying suppliers and sourcing materials from multiple locations
- Investing in technology and infrastructure to improve supply chain visibility and responsiveness
Question & Answer Hub
What is the customer’s customer?
The customer’s customer refers to the end-user or consumer who purchases the products or services from the customer.
Why is it important to consider the customer’s customer in supply chain management?
Considering the customer’s customer allows businesses to understand the ultimate demand for their products and services, identify potential pain points, and develop strategies to enhance customer satisfaction.
How can businesses manage upstream relationships to enhance customer satisfaction?
Businesses can manage upstream relationships by fostering collaboration, sharing information, implementing risk management strategies, and investing in innovation to create value for both customers and their customers.